Justine Cornelson of BrettYoung Seeds says verticillium is one reason Manitoba saw disappointing canola yields last year. The disease needs to be the subject of more research, since little has been done to date.


Disease is a relative newcomer to Canada and has been the subject of little research globally

Pushing a problem field to the front of the planting queue may help limit infection
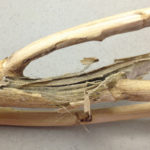
Verticillium and Goss’s wilt are both easily spotted near or after harvest




More than 90 per cent of surveyed canola fields had blackleg


Where it came from isn’t as important as how it will be contained when it comes to verticillium wilt in canola
